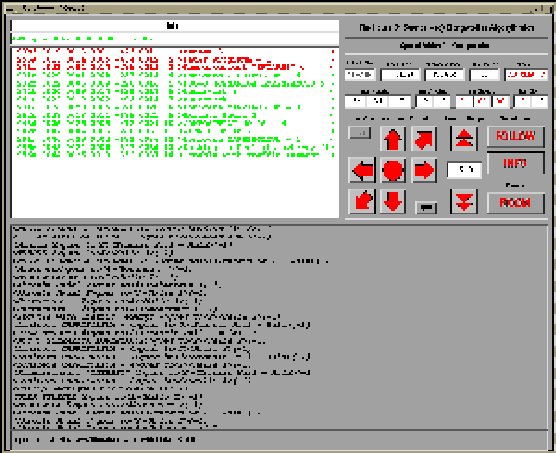
Software
Next: Audio System Up: NETART-EXPERIMENT-INSTALLATION Sound-Drifting - Linz Previous: Network Inhalt
Unterabschnitte
- Network-Tools
- Database
- Sound Rendering
- optional graphic/interaction server
- optional Multicast-Multi-path-Router
- Implementation
Software
Network-Tools
are the set of programs which define and control all the connectivity of the computers and therefore could be seen as the logistic part of the installation. It distributes streams in the system, connects independent Ethernet-segments, controls the throughput and reserves bandwidth for streams.
Database
A database which collects and distributes all information of over the systems and handles the FTP-upload directories and streams. It also ''makes'' the travel from one place of the overall system to another, preventing that streams do not overload the internal network and that they are switched to target computer. in generally are stored, and samples are taken out of streams (with csound-scripts) making new for mutation processes.
Sound Rendering
Takes the data from the database and renders them to a composition. A spatialisation is made according to the specific needs. So there are different render machines for 3D-Audio, roaming sounds and streams/radio.
optional graphic/interaction server
connects to a specific audio-rendering program and gets the information about all the used for current audio-rendering.
At the time there are three kinds of them, an MESA-GL (OPEN*GL) server, 2D Landscape (QT-graphics) and a ASCII (ncurses) interface (because of historical reasons) used for navigation and controlling the compositions.
For interaction there is a control panel (like a joystick) where interaction can take place and overall parameters can be changed. If there is no interaction, the system is switched to automatic mode.
optional Multicast-Multi-path-Router
Because of the Internet will be very overloaded (as seen in former years) on the days of the installation, because of the ars electronica festival, it would be useful to have a guaranteed bandwidth. Since the installation is critically depending on streams and interaction from outside this behavior should be controlled.
This could be done by an own line to the Internet. Additionally a multicast router should take care that incoming streams are split, so they have to be established only once per remote location. Also a remote multicast should split the out-stream somewhere else in the world, so there is only one out-stream needed to this multicast router.
Also the Web-server should be not at the location, but a save connection for updating him should be provided.
Implementation
The implementation of the software ends up with the program package . The use of this package can be adjusted to the actual needs and is distributed as source-code to be compiled on linux-machines (Intel, DEC/alpha) as well as on SGI-computer under IRIX.
A example of a previous implementation for is shown in figure 3 . A sequence of navigation screen-shots are shown in figure 4.
Next: Audio System Up: NETART-EXPERIMENT-INSTALLATION Sound-Drifting - Linz Previous: Network Inhalt HAss.DI Winfried Ritsch - ritsch@algo.mur.at