Hardware Manual MAAS-DSP-Board V0.9
- 0. Table of Contents
- 1.General Description
- 2. Files and Description
- 3. Configuration and I/O-Connectors
- 3.1 Jumpers
- 3.2 Address-Decoding
- 3.3 ESSI-Configuration-Latch
- 3.4 ESSI_1-Connector
- 3.5 ESSI_2-Connector
- 3.6 DSP-Bus-Expansion-Connector
- 3.7 MIDI-Connector
- 3.8 RS-232-Connector
- 3.9 DSP-JTAG-Connector
- 4. Assembling
- 4.1 Pre-Checking the PCB
- 4.2 Mounting and Soldering of Components (Part 1)
- 4.3 IC19-Patch
- 4.4 Checking the PCB (Part 1)
- 4.5 Testing the PCB by External Supply (Part 1)
- 4.6 Mounting-Options
- 4.6.1 Flash-PROM IC2
- 4.6.2 SRAM IC3...IC5
- 4.6.3 ESSI F1...F6, CON2, CON3, CON5, IC6...IC14
- 4.6.4 Opto-Coupler IC17, IC18, R8...R14, D1, CON7
- 4.6.5 DSP-Bus-Expansion CON4, CON6
- 4.7 Checking the PCB (Part 2)
- 4.8 Testing the PCB by External Supply (Part 2)
- 4.9 Plugging the PCB into a PCI-Slot
Hardware Manual of MAAS DSP Board Version 0.9 beta
0. Table of Contents
1. General Description
Project: D.I. Winfried Ritsch
Developed at: Institute of Electronic Music (IEM),
University of Music and dramatic Arts in Graz, Austria
The MAAS-DSP-Board and the I/O-Modules are part of the MAAS-Project.
The MAAS-hardware is divided into 3 groups:
- MAAS-DSP-Board (MAAB)
- Module-Interface-Boards
- I/O-Module-Boards (DAC, ADC)
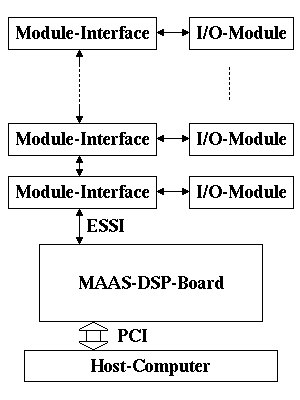
Several I/O-configurations of the ESSI are possible.
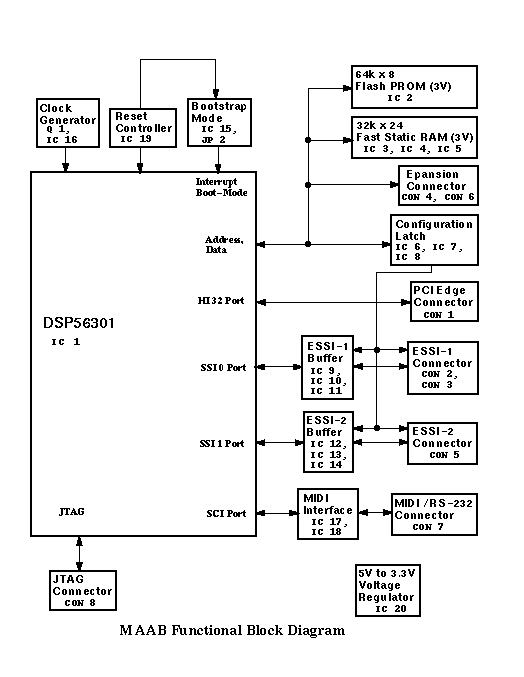
The schematic circuit diagram of MAAB is shown in 12 files: 6 post-script-files
for printing and 6 GIF-files for displaying.
The different layers of the printed circuit board layout are shown in 18 files: 9 post-script-files for printing and 9 GIF-files for displaying.
back to Table of Contents)
| Reference-Designator: | # | Value / Part-Description: | Package / Lead-
Dimension: |
| C1 | 1 | 390 pF, 50 V, SMD Ceramic-Multilayer Capacitor | Chip-Size 1206 |
| C2,C10.....C58,C62,C66, C68,C70,C72,C74 | 56 | 100 nF, 50 V, SMD Ceramic-Multilayer Capacitor | Chip-Size 1206 |
| C3,C4 | 2 | 22 pF, 50 V, SMD Ceramic-Multilayer Capacitor | Chip-Size 1206 |
| C6,C59,C63,C67,C69, C71,C73,C75......C8 | 14 | 47 µF, 16 V, Leaded Radial Aluminum-Electrolytic Capacitor | LS = 5mm |
| C7,C8 | 2 | 1.0 µF , 35 V, Leaded Radial Tantalum-Electrolytic Capacitor | LS = 5mm |
| C9 | 1 | 470 µF, 10 V, Leaded Axial Aluminum-Electrolytic Capacitor | LS < 20mm,
Diameter < 10mm |
| C60,C61,C64,C65, C82,C83 | 6 | 10 µF , 16 V, Leaded Radial Tantalum-Electrolytic Capacitor | LS = 5mm |
| C84.......C89 | 6 | 10 µF , 10 V, SMD-Chip Tantalum-Electrolytic-Capacitor | Chip-Size (l×w×h) =
6×3.2×2.5 mm |
| F1,F4 | 2 | RUE110, PTC-Multi-Fuse,
1.1A / 2.2 A, Leaded |
LS = 5mm |
| F2,F3,F5,F6 | 4 | RXE020, PTC-Multi-Fuse,
0.2A / 0.4 A, Leaded |
LS = 5mm |
| IC1 | 1 | DSP56301PW80,
Motorola 3.3V-DSP |
SMD TQFP208
(pdf-datasheet) |
| IC2 | 1 | AT29LV512-20JC, Atmel 3.3V-
Flash-PROM, 64k × 8, 200 ns |
SMD PLCC32
(pdf-datasheet) |
| IC3.....IC5 | 3 | UM61L256A-10, UMC 3.3V-
Fast-Static-RAM, 32k × 8, 10 ns |
UM61L256A-10, UMC 3.3V-Fast-Static-RAM,
32k × 8, 10 ns (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC6......IC8 | 3 | 74HCT377, Octal-D-FF + Enable,
Leaded |
DIL 20 (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC9,IC11,IC12,IC14 | 4 | 74HCT125, Quad-Line-Driver,
Leaded |
DIL 14 (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC10,IC13 | 2 | 74HCT126, Quad-Line-Driver,
Leaded |
DIL 14 (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC15 | 1 | 74HCT241, Octal-Bus-Driver | SMD SO20
(pdf-datasheet) |
| IC16 | 1 | Quartz-Oscillator, Leaded,16 MHz | Metal-Case, DIL8
(pdf-datasheet) |
| IC17 | 1 | PC900V, Optocoupler, Leaded | DIL 6 (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC18 | 1 | 74LS07, Hex-Buffer, Leaded | DIL14 (pdf-datasheet) |
| IC19 | 1 | MAX 811 LCUS-T, 5V-Under-Voltage-Sensor and Reset-Controller | SMD SOT-143
(pdf-datasheet MAX811) (pdf-datasheet MC34164) |
| IC20 | 1 | LT1085 CT-3.3, Linear-Techn. 3V3-Lowdrop-Voltage-Regulator, Leaded | TO 220
(pdf-datasheet) |
| IC17" | 1 | IC-Socket, Leaded | DIL6 |
| IC9".......IC14",IC18" | 7 | IC-Socket, Leaded | DIL14 |
| IC6"......IC8" | 3 | IC-Socket, Leaded | DIL20 |
| JP1,JP2, CON2.....CON6,CON8 | 2 | Dual-Pin-Array, 2×50 , Leaded, Vertical | LS = 2.54 mm |
| CON2 | 1 | SCSI-2-Socket, 50 poles, 90-Degree, Leaded | |
| CON7 | 1 | D-SUB-9-Socket, 9 poles , 90-Degree, Leaded, Female | |
| SW1 | 1 | Micro-Push-Button , 90-Degree, Leaded | |
| R1 | 1 | 680 k, Leaded Resistor | |
| R2.....R7,R9 | 7 | 10 k, SMD-Chip-Resistor | Chip-Size 1206 |
| R8 | 1 | 1k, Leaded Resistor | |
| R10.....R14 | 5 | 220 E, Leaded Resistor | |
| R17 | 1 | 150 E, Leaded Resistor | |
| RN1,RN3,RN5.....RN7 | 5 | 8×10k L09-1, Leaded Resistor-Array | SIL9 |
| RN2,RN4 | 2 | 8×1k L09-1, Leaded Resistor-Array | SIL9 |
| Q1 | 1 | Quartz , 17 MHz , Leaded, Vertical | Metal-Case, HC 18/U |
| D1 | 1 | 1N4148, Diode, 100 mA, 100 V , Leaded | |
| D3 | 1 | 1N5819, Schottky-Diode , Leaded | |
| LED1 | 1 | Green LED, Leaded | Diameter = 3mm |
For producing a PCB, you need 6 gerber-files and their aperture-files plus 1 excellon-drill-file and its drill-configuration-file. There are 2 solder-stop-files, 1 top-layer-file, 1 bottom-layer-file and 2 inner-layer-files in gerber-format. There is also one drill-file in excellon-format. All files are seen from top-view and not mirrored. The 2 solder-stop-files and the 2 inner-layer-files are displayed inversely. The order of the following gerber-files is the same as the arrangement of the layers in the PCB.
back to Table of Contents)
The board contains 5 Jumpers:
- Jumper-A: JP2 Pin 7 and Pin 8 Boot-Mode-Bit A (inserted:LOW / removed:HIGH);
- Jumper-B: JP2 Pin 5 and Pin 6 Boot-Mode-Bit B (inserted:LOW / removed:HIGH);
- Jumper-C: JP2 Pin 3 and Pin 4 Boot-Mode-Bit C (inserted:LOW / removed:HIGH);
- Jumper-P: JP2 Pin 1 and Pin 2 PLL-Enable-Bit (inserted:PLL is enabled / removed:PLL is disabled);
- Jumper-V: JP1 Pin 2 and Pin 3 Voltage-Clamp-Bit (inserted:for 3.3V-PCI / removed:for 5V-PCI).
The DSP56301 has 4 internal chipselect-pins:
- chipselect AA0 for external SRAM;
- chipselect AA1 for external Flash-PROM;
- chipselect AA2 for external 24-Bit-Latch;
- chipselect AA3 for Expansion-Board (e.g. DRAM).
AA1 selects 65536 × 8 Bit (Data-Bit 0 to 7) Read & Write;
AA2 selects 1 × 24 Bit Write-Only;
- Bit 00 : S1RFSDIRESSI1-Receive-Frame-Sync-DIRection
- Bit 01 : S1TCKDIRESSI1-Transmit-Clock-DIRection
- Bit 02 : S1TFSDIRESSI1-Transmit-Frame-Sync-DIRection
- Bit 03 : S1RCKDIRESSI1-Receive-Clock-DIRection
- Bit 04 : S1DT/CTLESSI1-Data/Control-qualifier
- Bit 05 : S1SRB0ESSI1-Sample-Rate-Bit-0
- Bit 06 : S1SRB1ESSI1-Sample-Rate-Bit-1
- Bit 07 : S1SRB2ESSI1-Sample-Rate-Bit-2
- Bit 08 : S2RFSDIRESSI2-Receive-Frame-Sync-DIRection
- Bit 09 : S2TCKDIRESSI2-Transmit-Clock-DIRection
- Bit 10 : S2TFSDIRESSI2-Transmit-Frame-Sync-DIRection
- Bit 11 : S2RCKDIRESSI2-Receive-Clock-DIRection
- Bit 12 : S2DT/CTLESSI2-Data/Control-qualifier
- Bit 13 : S2SRB0ESSI2-Sample-Rate-Bit-0
- Bit 14 : S2SRB1ESSI2-Sample-Rate-Bit-1
- Bit 15 : S2SRB2ESSI2-Sample-Rate-Bit-2
- Bit 16 : S1CTDXESSI1-Configuration-Transmit-Data
- Bit 17 : S1CCLKESSI1-Configuration-Clock
- Bit 18 : S1CTENESSI1-Configuration-Transmit-ENable
- Bit 19 : S1CRENESSI1-Configuration-Receive-ENable
- Bit 20 : S2CCLKESSI2-Configuration-Clock
- Bit 21 : S2CTENESSI2-Configuration-Transmit-ENable
- Bit 22 : S2CTDXESSI2-Configuration-Transmit-Data
- Bit 23 : S2CRENESSI2-Configuration-Receive-ENable
- LOW : DSP -> ESSI;
- HIGH : ESSI -> DSP;
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | S1-12V | - 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 2 | S1-12V | - 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 3 | S1+12V | + 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 4 | S1+12V | + 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | S1+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 8 | S1+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 9 | NC | not connected |
| 10 | NC | not connected |
| 11 | S1+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 12 | S1+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 13 | GND | Ground |
| 14 | RESERVED | Reseved for future-purpose |
| 15 | GND | Ground |
| 16 | RESERVED | Reseved for future-purpose |
| 17 | GND | Ground |
| 18 | S1TFS | Transmit-Frame-Sync (IO) |
| 19 | GND | Ground |
| 20 | S1RFS | Receive-Frame-Sync (IO) |
| 21 | GND | Ground |
| 22 | S1TCK | Transmit-Clock (IO) |
| 23 | GND | Ground |
| 24 | S1RCK | Receive-Clock (IO) |
| 25 | GND | Ground |
| 26 | S1TDX | Transmit-Data (OUT) |
| 27 | GND | Ground |
| 28 | S1RDX | Receive-Data (IN) |
| 29 | GND | Ground |
| 30 | S1CRDX | Configuration-Receive-Data (IN) |
| 31 | GND | Ground |
| 32 | S1RFSDIR | Receive-Frame-Sync-Direction (OUT) |
| 33 | S1RST | ESSI-Reset |
| 34 | S1TFSDIR | Transmit-Frame-Sync-Direction (OUT) |
| 35 | S1RCKDIR | Receive-Clock-Direction (OUT) |
| 36 | S1TCKDIR | Transmit-Clock-Direction (OUT) |
| 37 | S1DT/CTL | Data/Control-Qualifier (OUT) |
| 38 | S1SRB1 | Sample-Rate-Bit 1 (OUT) |
| 39 | S1SRB0 | Sample-Rate-Bit 0 (OUT) |
| 40 | S1SRB2 | Sample-Rate-Bit 2 (OUT) |
| 41 | GND | Ground |
| 42 | S1CTDX | Configuration-Transmit-Data (OUT) |
| 43 | GND | Ground |
| 44 | S1CTEN | Configuration-Transmit-Enable (OUT) |
| 45 | GND | Ground |
| 46 | S1CCLK | Configuration-Clock (OUT) |
| 47 | GND | Ground |
| 48 | S1CREN | Configuration-Receive-Enable (OUT) |
| 49 | GND | Ground |
| 50 | KEY | not connected and mechan. Key |
(back to Table of Contents)
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | S2-12V | - 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 2 | S2-12V | - 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 3 | S2+12V | + 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 4 | S2+12V | + 12 V Supply (200 mA Fuse) |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | S2+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 8 | S2+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 9 | NC | not connected |
| 10 | NC | not connected |
| 11 | S2+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 12 | S2+5V | + 5 V Supply (1 A Fuse) |
| 13 | GND | Ground |
| 14 | RESERVED | Reseved for future-purpose |
| 15 | GND | Ground |
| 16 | RESERVED | Reseved for future-purpose |
| 17 | GND | Ground |
| 18 | S2TFS | Transmit-Frame-Sync (IO) |
| 19 | GND | Ground |
| 20 | S2RFS | Receive-Frame-Sync (IO) |
| 21 | GND | Ground |
| 22 | S2TCK | Transmit-Clock (IO) |
| 23 | GND | Ground |
| 24 | S2RCK | Receive-Clock (IO) |
| 25 | GND | Ground |
| 26 | S2TDX | Transmit-Data (OUT) |
| 27 | GND | Ground |
| 28 | S2RDX | Receive-Data (IN) |
| 29 | GND | Ground |
| 30 | S2CRDX | Configuration-Receive-Data (IN) |
| 31 | GND | Ground |
| 32 | S2RFSDIR | Receive-Frame-Sync-Direction (OUT) |
| 33 | S2RST | ESSI-Reset |
| 34 | S2TFSDIR | Transmit-Frame-Sync-Direction (OUT) |
| 35 | S2RCKDIR | Receive-Clock-Direction (OUT) |
| 36 | S2TCKDIR | Transmit-Clock-Direction (OUT) |
| 37 | S2DT/CTL | Data/Control-Qualifier (OUT) |
| 38 | S2SRB1 | Sample-Rate-Bit 1 (OUT) |
| 39 | S2SRB0 | Sample-Rate-Bit 0 (OUT) |
| 40 | S2SRB2 | Sample-Rate-Bit 2 (OUT) |
| 41 | GND | Ground |
| 42 | S2CTDX | Configuration-Transmit-Data (OUT) |
| 43 | GND | Ground |
| 44 | S2CTEN | Configuration-Transmit-Enable (OUT) |
| 45 | GND | Ground |
| 46 | S2CCLK | Configuration-Clock (OUT) |
| 47 | GND | Ground |
| 48 | S2CREN | Configuration-Receive-Enable (OUT) |
| 49 | GND | Ground |
| 50 | KEY | not connected and mechan. Key |
CON4:
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | +3V | +3.3 V Supply |
| 2 | +5V | +5 V Supply |
| 3 | +3V | +3.3 V Supply |
| 4 | +5V | +5 V Supply |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | DA12 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 12 (OUT) |
| 8 | /WR | Write-Enable (OUT) |
| 9 | DA7 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 7 (OUT) |
| 10 | DA14 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 14 (OUT) |
| 11 | DA6 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 6 (OUT) |
| 12 | DA13 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 13 (OUT) |
| 13 | DA5 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 5 (OUT) |
| 14 | DA8 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 8 (OUT) |
| 15 | DA4 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 4 (OUT) |
| 16 | DA9 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 9 (OUT) |
| 17 | DA3 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 3 (OUT) |
| 18 | DA11 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 11 (OUT) |
| 19 | DA2 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 2 (OUT) |
| 20 | /RD | Read-Enable (OUT) |
| 21 | DA1 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 1 (OUT) |
| 22 | DA10 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 10 (OUT) |
| 23 | DA0 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 0 (OUT) |
| 24 | AA1 | Chipselect (OUT) |
| 25 | DD6 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 6 (IO) |
| 26 | DD7 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 7 (IO) |
| 27 | DD3 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 3 (IO) |
| 28 | DD5 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 5 (IO) |
| 29 | DD4 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 4 (IO) |
| 30 | DD1 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 1 (IO) |
| 31 | DD0 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 0 (IO) |
| 32 | DD2 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 2 (IO) |
| 33 | DA22 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 22 (OUT) |
| 34 | DA23 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 23 (OUT) |
| 35 | DA20 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 20 (OUT) |
| 36 | DA21 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 21 (OUT) |
| 37 | DA18 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 18 (OUT) |
| 38 | DA19 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 19 (OUT) |
| 39 | DA16 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 16 (OUT) |
| 40 | DA17 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 17 (OUT) |
CON6:
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | AA3 | Chipselect (OUT) |
| 2 | DA15 | DSP-Address-Bus-Bit 15 (OUT) |
| 3 | /BG | Bus-Grant (IN) |
| 4 | /BR | Bus-Request (OUT) |
| 5 | /BB | Bus-Busy (IO) |
| 6 | /TA | Transfer-Acknowledge (IN) |
| 7 | CLKOUT | synchr. DSP-Clock (OUT) |
| 8 | /CAS | Column-Address-Strobe (OUT) |
| 9 | AA0 | Chipselect (OUT) |
| 10 | DD17 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 17 (IO) |
| 11 | /BS | Bus-Strobe (OUT) |
| 12 | /BL | Bus-Lock (OUT) |
| 13 | /RESET | Board-Reset (OUT) |
| 14 | AA2 | Chipselect (OUT) |
| 15 | KEY | not connected and mechan. Key |
| 16 | DD9 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 9 (IO) |
| 17 | DD8 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 8 (IO) |
| 18 | DD11 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 11 (IO) |
| 19 | DD10 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 10 (IO) |
| 20 | DD20 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 20 (IO) |
| 21 | DD16 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 16 (IO) |
| 22 | DD21 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 21 (IO) |
| 23 | DD22 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 22 (IO) |
| 24 | DD23 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 23 (IO) |
| 25 | DD12 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 12 (IO) |
| 26 | DD14 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 14 (IO) |
| 27 | DD13 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 13 (IO) |
| 28 | DD18 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 18 (IO) |
| 29 | DD15 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 15 (IO) |
| 30 | DD19 | DSP-Data-Bus-Bit 19 (IO) |
| 31 | EX/IRQB | Extern. Interrupt-Reqest B (IN) |
| 32 | EX/IRQA | Extern. Interrupt-Reqest A (IN) |
| 33 | EX/NMI | Nonmask. Interrupt (IN) |
| 34 | EX/IRQC | Extern. Interrupt-Reqest C (IN) |
| 35 | GND | Ground |
| 36 | GND | Ground |
| 37 | +3V | +3.3 V Supply |
| 38 | +5V | +5 V Supply |
| 39 | +3V | +3.3 V Supply |
| 40 | +5V | +5 V Supply |
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | +MIDI_IN | Midi-In (Current In) |
| 2 | -MIDI_IN | Midi-In (Current Out) |
| 3 | +MIDI_OUT | Midi-Out (Current Out) |
| 4 | -MIDI_OUT | Midi-Out (Current In) |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | +MIDI_THR | Midi-Through (Current Out) |
| 7 | -MIDI_THR | Midi-Through (Current In) |
| 8 | GND | Ground |
| 9 | NC | not connected |
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | NC | not connected |
| 2 | +RDX | Receive Data from Interface to DSP (IN) |
| 3 | +TDX | Transmit Data from DSP to Interface (OUT) |
| 4 | NC | not connected |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | NC | not connected |
| 7 | NC | not connected |
| 8 | GND | Ground |
| 9 | NC | not connected |
| Pin: | Signal-Name: | Signal-Description: |
| 1 | TDI | Test-Data-Input (IN) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TDO | Test-Data-Output (OUT) |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
| 5 | TCK | Test-Clock (IN) |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | NC | not connected |
| 8 | KEY | not connected and mechan. Key |
| 9 | /RESET | DSP-Reset (OUT) |
| 10 | TMS | Test-Mode-Select (IN) |
| 11 | +3V | +3.3 V Supply |
| 12 | NC | not connected |
| 13 | /DE | Debug-Event (IO) |
| 14 | /TRST | Test-Reset (IN) |
Provided that the DSP is already mounted on the MAAB-PCB,
check the resistance of the following signals with an ohmmeter:
- +5V to +3V ....... infinite
- +5V to Ground ....... infinite
- +3V to Ground ....... medium resistance
- +12V to Ground ....... infinite
- -12V to Ground ....... infinite
Make sure that the higher potential of the ohmmeter is connected to the higher potential in the circuit and vice versa.
The order of potentials in the circuit is:
- +12V
- +5V
- signals of components supplied with +5V
- +3V
- signals of components supplied with +3V
- Ground
- -12V
- IC1....IC5 : +3V
- IC6....IC19 : +5V
- IC20 : +5V and +3V
If all previous measurements were correct, you should mount and solder the following components:
- The SMD-Chip-Capacitors C1 .... C4; C14; C16 .... C19; C25 .... C52; C54 .... C56; do not mount C5 (see IC19-Patch). Notice that these Capacitors have no mark, so pay attention that you don't get them mixed up. They have no polarity.
- The leaded Capacitors C6 .... C9; C75 .... C81; C85 .... C89. The Aluminum-Electrolytic Capacitors are marked at their "minus"-pins, the Tantalum-Electrolytic Capacitors are marked at their "plus"-pins, the Capacitors in the component-placing-sheets are marked at their "plus"-pins.
- The Resistor-Arrays RN1 .... RN3 and RN5 .... RN7. If you did not get the arrays with 6 Resistors, you can cut off the last 2 Resistors of an array with 8 (attention: not the marked end).
- The Resistors R1 and R2; R4 .... R7; R17; do not mount R15 and R16 (see IC19-Patch).
- The Diode D3; the LED LED1 (the longer pin is the "plus"-pin); do not mount D2 (see IC19-Patch). The drill-holes for D3 in the PCB are too small, so you have to bend the leads of D3 and then to cut them off very short (like an SMD). Now you can solder D3 like an SMD.
- SW1, IC15 and IC20 (first fix IC20 with an M3 screw, then solder it).
- IC16; if IC16 is available only in a DIL-14 case, you should extend and bend the 2 leads of pin 1 and pin 14.
- Q1; if Q1 is not available in 1/3-case-height, you should mount Q1 flat on top of IC1, connecting and fixing the case with a 0.5 mm wire to Ground (use the Ground-Via of C3 and C4).
- JP1, JP2, CON8. The usual size of Pin-Arrays is 2×50, you need 2 of them. You have to divide them into 2×20- + 2×20- + 2×4- + 2×3- + 2×3-parts and 2×20- + 2×20- + 2×4- + 2×4- + 2×1- + 2×1-parts (with a fine saw). (see Mounting-Options)
- JP1 : 2×1-Pin-Array to Pin 2 and 3;
- JP2 : 2×4-Pin-Array;
- CON3 : 2×20-Pin-Array + in between 2×1-Pins leave out + 2×4-Pin-Array;
- CON4 : 2×20-Pin-Array;
- CON5 : 2×20-Pin-Array + in between 2×1-Pins leave out + 2×4-Pin-Array;
- CON6 : 2×20-Pin-Array;
- CON8 : 2×3-Pin-Array + in between 2×1-Pins leave out + 2×3-Pin-Array.
(see ESSI F1...F6, CON2, CON3, CON5, IC6...IC14) (see DSP-Bus-Expansion CON4, CON6)
IC19 was changed: a MAX811CUS-T was used instead of an MC34164. Therefore, you have to patch the circuit around IC19. First you should mount and solder the MAX811CUS-T with its Pins 3 and 4 on the unused Pads 5 ... 8 of IC19. Then you should bridge R15 and patch the following connections with a thin wire:
- IC19-Pad4 to MAX811-Pin1 (Ground);
- IC19-Pad2 to MAX811-Pin3 (Master-Reset-Input);
- IC19-Pad1 to MAX811-Pin2 (Reset-Output);
- C84-Pad +5V to MAX811-Pin4 (Vcc).
- +5V to +3V ............ medium resistance
- +5V to Ground ....... medium resistance
- +3V to Ground ....... medium resistance
The same measuring-rules as in Pre-Checking the PCB are valid. The MAAB should first be tested stand-alone. You have to solder 2 insolated wires (red and black) to IC20 Pin 1 (Ground = black) and to IC20 Pin 3 (+5V = red). Insert only Jumpers A, C and P (SCI-Bootstrap).
You should own a Voltage-regulated Power-Supply with variable Current-Control.
Adjust the voltage to 5V, the current-control to minimum (about 1 mA) and connect the 2 supply-wires of the PCB to the supply correctly. Then slowly increase the current-control up to 200 mA while you measure the voltage between +3V and Ground (IC20 Pin 2 and 1). The voltage should have 3.3 V , the current of the board should be less than 150 mA. LED1 should give a green light. After pushing SW1, IC15 Pin 1 should be LOW for a short time (min. 140 ms) and afterwards HIGH (5V).
If you have an Oscilloscope, you can check 2 Clock-Signals; at CON6 Pin 7 you should measure a 17 MHz / 3.3 V peak to peak signal; at IC16 Pin 5 (Pin 8 respectivly) you should measure a 16 MHz / 5 V peak to peak signal.
If the previous measurements were correct, you can continue to mount components on the PCB.- Stand-alone with external Supply and Flash-Bootstrap
- PCI-Plug-In with Flash-Bootstrap
- PCI-Plug-In with Host-Bootstrap and Flash-Memory
- PCI-Plug-In with Host-Bootstrap and without Flash-Memory
Mount and solder IC2 and C10 (after testing: insert only Jumpers B, C and P).
Mount and solder IC2 and C10 (after testing: insert only Jumpers B, C and P).
Mount and solder IC2 and C10 (after testing: insert only Jumpers A, B and P).
nothing (after testing: insert only Jumpers A, B and P) (see Jumpers).
- Low-Memory-Version
- High-Memory-Version
nothing.
Mount and solder IC3 .... IC5 and C11 .... C13.
- ESSI 1 without Supply and without SCSCI-2 CON2
- ESSI 1 without Supply and without DIL-Pin-Array CON3
- ESSI 1 without Supply and with CON2 and CON3
- ESSI 1 with Supply and without SCSCI-2 CON2
- ESSI 1 with Supply and without DIL-Pin-Array CON3
- ESSI 1 with Supply and with CON2 and CON3
- without ESSI 2
- ESSI 2 without Supply
- ESSI 2 with Supply
Mount and solder CON3, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket, IC9 ... IC11
and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, ESSI2-option.
Mount and solder CON2, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket, IC9 ... IC11
and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, ESSI2-option.
Mount and solder CON2 and CON3, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket,
IC9 ... IC11 and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, ESSI2-option.
Mount and solder CON3, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket, IC9 ... IC11
and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, F1 ... F3, C58 .... C61, C82, C83, ESSI2-option.
Mount and solder CON2, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket, IC9 ... IC11
and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, F1 ... F3, C57, C59 .... C61, C82, C83, ESSI2-option.
Mount and solder CON2 and CON3, IC6 and DIL-20-socket, IC8 and DIL-20-socket, IC9 ... IC11
and their DIL-14-sockets, C14, C16 .... C19, F1 ... F3, C57 .... C61, C82, C83, ESSI2-option.
nothing but ESSI1-option.
Mount and solder CON5, IC7 and DIL-20-socket, IC12 ... IC14 and their DIL-14-sockets,
RN4, C15, C20 .... C22, C53, ESSI1-option.
Mount and solder CON5, IC7 and DIL-20-socket, IC12 ... IC14 and their DIL-14-sockets,
RN4, C15, C20 .... C22, C53, F4 ... F6, C62 .... C65, C82, C83, ESSI1-option
(see Mounting and Soldering of Components (Part 1) last item).
- neither MIDI nor RS-232
- MIDI
- RS-232
nothing.
Mount and solder IC17 and DIL-6-socket; D1 and R8 .... R14; IC18 and DIL-14-socket; C24 and C74; CON7. The drill-holes for CON7 in the PCB are too small, so you have to press the leads of CON7 a little bit flatter with a pair of pliers.
First you have to patch the circuit around IC17, IC18 and CON7. Cut through the trace between CON7 Pin 3 and Via (to IC18 Pin 3); cut through the trace between CON7 Pin 6 and R14 (both on bottom-side of the PCB). Instead of a 220 ohm resistor, use a 10 kohm resistor for R13. Patch CON7 Pin 2 to IC18 Pin 3;patch IC18 Pin 4 to IC17 Pin 4; patch IC18 Pin 6 to CON7 Pin 3; patch CON7 Pin 3 to R14 (the Pin which was cut through with CON7 Pin 6). Solder all patches on the bottom-side of the PCB with a thin wire. Mount and solder R8, R9, R13 and R14; IC18 and DIL-14-socket; C24 and CON7. The drill-holes for CON7 in the PCB are too small, so you have to press the leads of CON7 a little bit flatter with a pair of pliers.
- with Expansion-Connector
- without Expansion-Connector
Mount and solder CON4 and CON6; C66 .... C73
(see Mounting and Soldering of Components (Part 1) last item).
nothing.
Now you should check several connections on board again:
- +5V to +3V ............ medium resistance
- +5V to Ground ....... medium resistance
- +3V to Ground ....... medium resistance
The same measuring rules as in Pre-Checking the PCB are valid. The MAAB should be tested stand-alone again. Follow the same procedure as in
Testing the PCB by External Supply (Part 1) . Only the supply-current will increase to 200 mA. description is in progress. ...
(back to Table of Contents)

